What Best Describes Smooth Muscle Cells
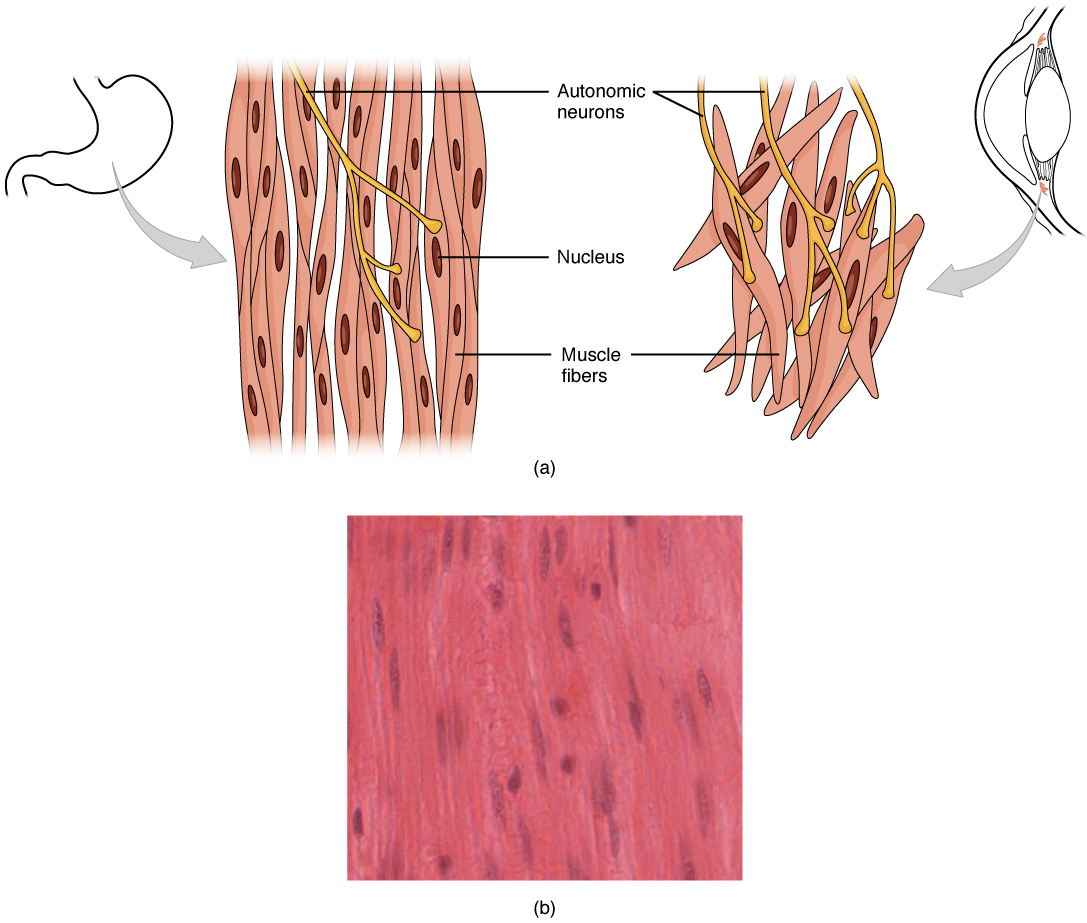
Smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and are spindle-shaped. However smooth muscle can be found throughout the body but is most common around the digestive tract in the walls of blood vessels arteries and.
13 15 Smooth Skeletal And Cardiac Muscles Biology Libretexts
Smooth muscle is the involuntarily controlled muscle.
. Ill be helping you with the 21st problem of the Chapter 29 problem set and 21 is asking which answer best describes the function of smooth muscle tissue. They primarily use anaerobic metabolism. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by a framework of other proteins.
1 To regain shape. Non-striated voluntary fast contraction D. They cannot exhibit tetanus.
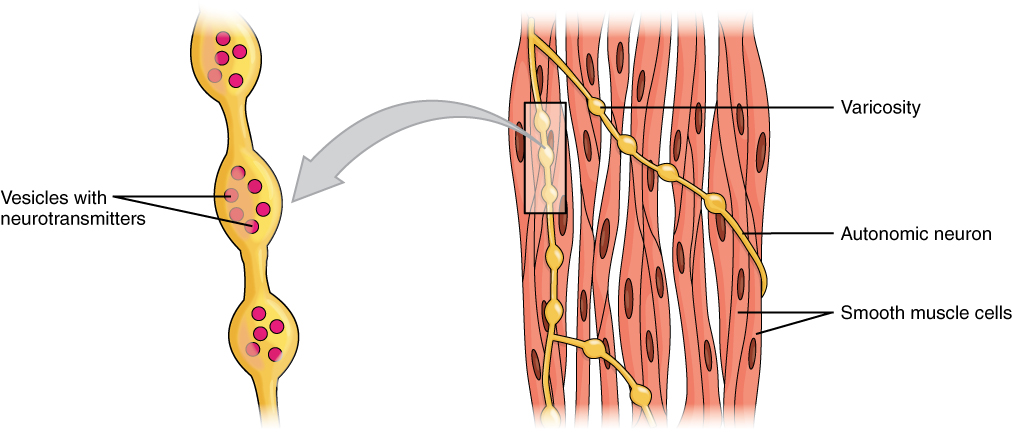
Smooth muscle cells. Which of the following choices correctly describes a key feature of smooth muscle tissue which is not present in skeletal or cardiac muscle. Involuntary branching intercalated discs autorhythmic varicosities D.
Rely on neuromuscular varicosities Voluntarily controlled d. So lets go through the best ones and pick it so we have. Smooth Muscle Definition.
They are resistant to fatigue. They have a rapid onset of contractions. It can recoil back to its original length due to elastic fibers.
C cardiac muscle uses little anaerobic fermentation. This includes Ca channel openers subthreshold depolarization and a variety of tissue factors and circulating hormones that stimulate the release of intracellular Ca stores. Smooth muscle cells can undergo hyperplasia mitotically dividing to produce new cells.
None of the above. Smooth muscle contraction is heavily Ca dependent. Cardiac muscle cells have an irregular branched appearance that are shorter than the longer cylindrical cells found in skeletal muscle tissue and different from the fusiform shape of smooth.
They have a rapid onset of contractions. Smooth muscle is the involuntarily controlled muscle. Depolarization of a smooth muscle cell whether it is autorhythmic or contractile is the result of A a decrease in K efflux B an increase in K efflux C.
It it stimulates contraction of the heart. Smooth muscles are non-striated muscle whose movement and contraction occurs involuntarily. Involuntary single nucleated non branching no sarcomeres single innervation B.
Smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue which is used by various systems to apply pressure to vessels and organs. Smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and are spindle-shaped. From which embryonic cell type does muscle tissue develop.
Smooth muscle is found throughout the body around various organs and tracts. Science Biology Anatomy Physiology Which of the following statements describes smooth muscle cells. What best describes the cells of unitary smooth muscle.
Smooth muscle tissue contraction is responsible for involuntary movements in the internal organs. Smooth muscle is found throughout the body around various organs and tracts. In unitary smooth muscle the cells are connected by gap junctions and are controlled.
Smooth muscle cells are arranged together in sheets and this organisation means that they can contract simultaneously. It forms the contractile component of the digestive urinary and reproductive systems as well as the airways and blood vessels. The structure and function of smooth muscle in all these organs are same except its stimuli.
Which of the following best describes smooth muscle. Striated voluntary fast contraction B. Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells.
Which of the following statements describes smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells are elastic not striated spindle-shaped and contain a single central nucleus. Find step-by-step Anatomy and physiology solutions and your answer to the following textbook question.
A it stays in place because elastic recoil occurs only after calcium is pumped back into the T-tubules. They have a rapid onset of contractions. I hope all is well today.
22The following best describes visceral smooth muscle cells and its innervation A. They are resistant to fatigue. 2 in explanations 1 A muscle can return to its original length when relaxed due to a quality of muscle tissue called elasticity.
None of the above. Which of the following statements describes smooth muscle cells. They cannot exhibit tetanus.
They have poorly developed sarcoplasmic reticulums and do not contain T-tubules due to the restricted size of. It affects the blood flow and blood pressure which could be possible like veins and arteries. Such muscle forms the wall of blood vessel uterus urinary bladder reproductive tracts and many more.
Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. Smooth muscle cells can undergo hyperplasia mitotically dividing to produce new cells. Smooth muscle is a type of non-striated muscle that is common in the walls of hollow organs and blood vessels.
Non-striated involuntary slow contraction E. Striated involuntary slow contraction C. B it stays in place because collagenous fibers hold the filaments in place.
Each cell is spindle shaped with a single nucleus and no visible striations Figure 441 Muscle Tissue. They are resistant to fatigue. They cannot exhibit tetanus.
C it stays in place because hundreds of other myosin heads are still attached. In unitary smooth muscle the cells are connected by gap junctions and are controlled by. Smooth muscle contraction uses less energy and lasts longer compared to that of skeletal muscle.
They primarily use anaerobic metabolism. They primarily use anaerobic metabolism. Which shape best describes cardiac muscle cells.
2Gross motor skills pertain to skills involving large muscle movements such as independent sitting crawling walking or running. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. The contraction of muscle is involuntary and occurs very rapidly.
Voluntary multinucleated intercalated discs single innervation C. Smooth muscle contractions of the viscera are the result of depolarization events induced by the interstitial cells of Cajal a type of autorhythmic smooth muscle cell. The answer is b branched.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1951/hAji9x7UR1SrWXVI9xqW3A_histology-smooth-muscle_english.png)
Smooth Muscle Structure Function Location Kenhub
No comments for "What Best Describes Smooth Muscle Cells"
Post a Comment